Impact of Subsea Mining on Bunker Fuel Demand
Subsea mining represents a burgeoning industry aimed at extracting minerals from the ocean floor, poised to influence global bunker fuel demand significantly. This article explores the potential ramifications of subsea mining operations on bunker fuel consumption, considering technological advancements, environmental concerns, and regulatory frameworks that shape the maritime sector.
Understanding Subsea Mining Operations
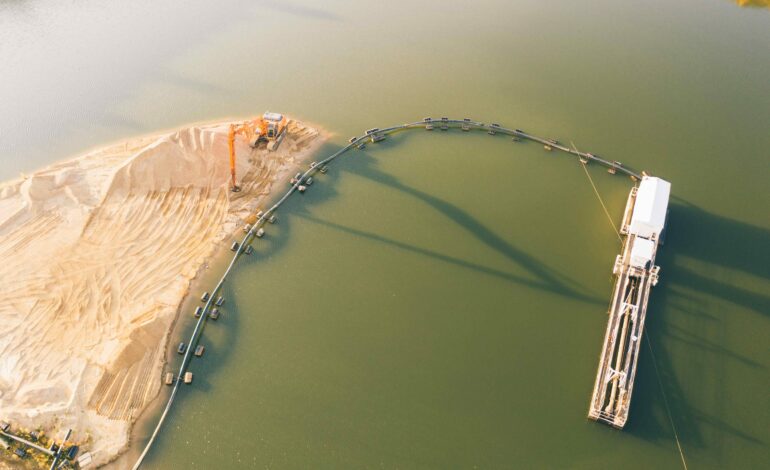
- Technological Advancements: Subsea mining relies on cutting-edge technologies such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) equipped with advanced sensors and robotic arms. These innovations enable the extraction of valuable minerals like polymetallic nodules and hydrothermal vent deposits from deep-sea environments.
- Resource Potential: The ocean floor holds vast reservoirs of untapped mineral resources critical for renewable energy technologies, electric vehicle batteries, and electronics manufacturing. Subsea mining is increasingly viewed as a sustainable solution to meet the escalating global demand for these essential minerals.
Impact on Bunker Fuel Demand
- Maritime Transport Logistics:
- Fuel Requirements: Subsea mining operations involve the transportation of heavy mining equipment, ROVs, and extracted minerals to and from remote mining sites. This logistical process significantly increases the demand for bunker fuels used by support vessels and in associated logistics operations.
- Distance and Accessibility: Mining locations are often situated far offshore and in deep-sea environments, necessitating extended voyages that consume substantial amounts of bunker fuel.
- Energy Intensity and Operational Efficiency:
- Power Generation: Bunker fuels play a pivotal role in powering subsea mining vessels and support ships, providing propulsion and onboard electricity generation crucial for sustaining mining operations.
- Efficiency Measures: To mitigate bunker fuel consumption and reduce environmental impact, industry efforts focus on adopting fuel-efficient technologies, integrating hybrid propulsion systems, and exploring energy storage solutions.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
- Ecosystem Impacts: Subsea mining activities have the potential to disturb marine habitats, impact biodiversity, and generate sediment plumes. Environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and rigorous mitigation strategies are essential to minimize these ecological consequences and ensure sustainable resource extraction practices.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Robust international regulations, overseen by bodies like the International Seabed Authority (ISA), govern exploration and exploitation activities in the international seabed area. These frameworks aim to uphold environmental protection standards and promote responsible resource management practices.
Future Trends and Mitigation Strategies
- Adoption of Alternative Energy Sources: Embracing cleaner fuels such as LNG (liquefied natural gas) and hydrogen presents opportunities to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with subsea mining operations, aligning with global sustainability objectives.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in autonomous operations, digitalization, and real-time monitoring technologies hold promise for enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing fuel consumption, and bolstering environmental stewardship in subsea mining endeavors.
Conclusion
Subsea mining holds immense promise for accessing critical minerals essential for modern technologies while addressing global resource demands. However, it also presents challenges related to bunker fuel consumption and environmental impact. By prioritizing sustainable practices, embracing technological innovations, and adhering to stringent regulatory frameworks, the maritime industry can navigate these challenges effectively and promote responsible subsea mining operations for a sustainable future.